So, you’ve heard of RAG chatbots and maybe even used one — but ever wondered how they actually work behind the scenes?
Let me guess — you asked a chatbot a super-specific question and it gave you an answer that felt like it had actually read your textbook, your company docs, or that 100-page PDF you uploaded. You sat back and thought, “Okay… how did it do that?”
You’re not alone. Most people assume it’s magic or some secret sauce only tech giants understand.
But here’s the truth: it’s not magic — it’s RAG. And once you get it, you’ll start seeing these bots in a whole new light.
So grab your curiosity (and maybe a coffee), and let’s unravel how RAG chatbots actually work — one simple step at a time.
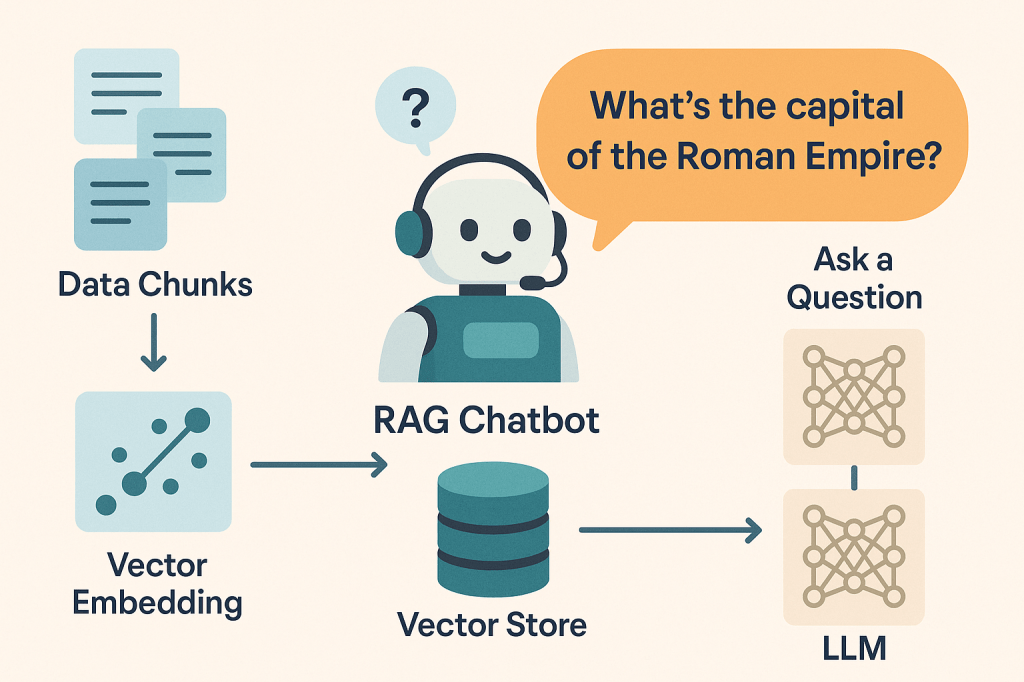
Step 1: It All Starts With a Huge Pile of Data
Imagine you’ve got a big textbook, a bunch of PDFs, or even a mountain of .txt files. That’s your raw data.
But here’s the thing: AI doesn’t just look at the whole book and go, “Okay, I get it.”
That would be like asking someone to memorize an entire encyclopedia in one go.
So what do we do instead?
Step 2: Slice It Up Into Chunks
Instead of feeding the whole book to the AI, we break it into smaller, bite-sized pieces.
Think of it like cutting a pizza into slices. Each chunk is a small piece of the whole — maybe a paragraph or a few sentences.
This process is called chunking, and it helps the AI understand context better and retrieve relevant info faster later on.
Step 3: Turn Chunks Into Math — a.k.a. Embeddings
Here’s where it gets really cool.
Each chunk gets passed through an embedding model, which transforms it into a vector — basically, a long list of numbers that capture the meaning of the chunk.
You can think of it like giving each chunk a unique fingerprint.
Step 4: Store Everything in a Special Library
Now that we have all our chunks and their number-fingerprint embeddings, we store them in a vector database.
This is like a super-smart library. Instead of organizing info by title or chapter, it organizes by meaning.
So even if your query doesn’t use the same words as the data, it can still find the right info.
Step 5: Ask a Question (The Query)
Now it’s your turn. Say you ask the chatbot:
“What’s the salary of Elon Musk?”
The chatbot doesn’t just guess or Google it. It follows a clever path…
Step 6: Your Question Becomes a Vector Too
Just like with the chunks earlier, your question also gets embedded — turned into a vector that represents what it means.
Now both your question and all the stored content are in the same language: vectors.
Step 7: Find the Closest Matches
Using vector similarity, the chatbot searches the vector database for chunks that are most similar to your query.
Basically, it’s asking:
“Which parts of the data are talking about something similar to this question?”
Boom! It finds the top matches — the most relevant chunks of information.
Step 8: Send It to the LLM for the Final Answer
Now, we combine your question and the top relevant chunks and send them to a Large Language Model (LLM) like GPT.
The LLM reads the context, understands the question, and crafts a clear, intelligent answer — just like magic (but smarter).
Let’s recap the RAG flow:
- Load your data (text, PDFs, docs).
- Chunk the content into smaller parts.
- Turn each chunk into a vector (embedding).
- Store everything in a vector database.
- Embed your question too.
- Search for similar chunks using vector similarity.
- Send the question + chunks to the LLM.
- Get a contextual, accurate answer.
That’s RAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation. It sounds fancy, but really, it’s just building a super-smart search system that feeds the right info to a powerful language model.
Hope this helped you see what’s going on behind the scenes!
Got more questions? Want another concept explained? Just shout!





Leave a comment